Comparison of Automatic Sliding Door and Automatic Revolving Door
Automatic Sliding Door and Automatic Revolving Door are the 2 key products and hot sale doors from TSTC Automatic Doors. Do you know the big differences from these 2 type of doors ? Here is the answer as below .

▪ Automatic Sliding Doors
Definition: Doors that open horizontally via motor-driven tracks, commonly used in commercial and healthcare settings.
Advantages:
Space Efficiency: Ideal for limited spaces, telescopic (foldable) designs maximize opening width while minimizing footprint.
Smooth surfaces (stainless steel/glass) resist corrosion and enable easy disinfection.
Safety & Accessibility: Force-sensitive reversal stops or reverses upon collision, reducing injury risks. Non-contact operation via sensors/buttons supports infection control.
Energy Savings: Rapid closing minimizes air exchange, cutting HVAC costs.
Low Noise: PWM-driven motors and silent tracks (<49 dB) suit quiet environments.
Disadvantages:
Limited Flow Capacity: Smaller openings may cause bottlenecks during peak traffic.
Reduced Wind Resistance: Less effective in high-wind areas compared to revolving doors.
Dependency on Tracks: Debris accumulation in tracks can disrupt operation, requiring frequent maintenance.
Key Applications:
Healthcare: Operating rooms, isolation wards, Hospitals, pharmaceutical facilities.
Laboratories/Cleanrooms: Spaces demanding strict contamination control.
Offices/Retail: Entrances with space constraints or moderate foot traffic.
▪ Automatic Revolving Doors
Definition: Rotating doors with 2–4 wings, typically installed at high-traffic building entrances.
Advantages:
Energy Efficiency:"Always open, always closed" design reduces air infiltration by >30%, maintaining indoor temperatures.
Critical for climates with extreme heating/cooling demands.
Wind & Weather Resistance: Seals against drafts, rain, and dust, enhancing lobby comfort.
Aesthetic Prestige: Creates a luxurious entrance for hotels, corporate towers, and upscale retail.
Crowd Management: Controls flow rate (e.g., a 2m-diameter door handles ~2,400 people/hour).
Advanced Safety Features:Anti-pinch sensors, emergency brakes, and foldable wings for evacuation.
Disadvantages:
High Costs: 3–5× more expensive than sliding doors due to complex mechanics.
Accessibility Challenges: Difficult for wheelchairs, strollers, or large luggage; requires supplemental side doors.
Maintenance Demands: Frequent servicing needed for sensors, motors, and seals.
Emergency Limitations: Despite foldable wings, panic during evacuations may cause jams.
Noise Issues: Motor/rotation sounds can disrupt quiet settings (e.g., libraries).
Key Applications:
Hospitality: Luxury hotels, resorts, and convention centers.
Corporate/Public Buildings: Skyscrapers, banks, and airports.
Shopping Malls: High-end retail entrances.
▪ Summary Comparison
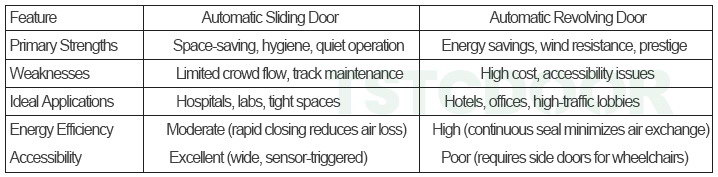
▪ Conclusion
Choose sliding doors for hygiene-critical or space-limited sites (e.g., labs, hospitals). Opt for revolving doors in energy-sensitive, high-prestige entrances with heavy traffic (e.g., hotels, offices). Pairing both types-e.g., revolving doors with sliding emergency exits-optimizes efficiency and safety .
 Development Trends of Automati
Development Trends of Automati
 Why The Qty. of Revolving Door
Why The Qty. of Revolving Door
 Why More Buildings Choose Tele
Why More Buildings Choose Tele
 Active Radar vs. Passive Radar
Active Radar vs. Passive Radar

